Table of Contents:
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
Core Concepts of Artificial Intelligence
Examples of Artificial Intelligence
Applications of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence Jobs and Career Opportunities
Benefits of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence Resources
Conclusion and Future of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence is no longer a fad, it is shaping how we perceive life, treat our work, and interact with the world around us. In this blog, we will explore the fascinating journey of artificial intelligence, its origin, core principles, real-world applications, and future implications.
1. Introduction to Artificial intelligence:
AI mainly involves the creation of various types of machines and algorithms that can perform tasks that require human intelligence. These tasks include problem-solving, perception and decision-making, understanding language, pattern recognition, and many more.
At its core, AI aims to simulate human thought processes enabling learning experiences and performing the same task through new input. Such machines are capable of receiving very huge data through machine learning with natural language processing (NLP) and computer vision.
The influence of AI is profound, spanning industries such as healthcare, finance, education, and entertainment. Algorithms manage what is fed to social media feeds and self-driving vehicles pave the way for intelligent personal assistants, such as Siri and Alexa to build a new future path in how we live, work, and play.
History and Evolution of AI:

Picture Courtesy: analyticsjobs.in
The journey of AI began long before it became a household term, rooted in philosophical questions about the nature of intelligence and the potential of machines. Here’s a brief look at its evolution:
1950s: The Birth of AI
Alan Turing’s significant question “Can machines think?” gave added impetus to the idea of AI. His Turing Test became a measure for judging the ability of a machine to simulate intelligent behavior. The Dartmouth Conference of 1956 marked the beginning of AI as an area of study, where scientists explored symbolic reasoning and problem-solving.
1960s–1970s: Early AI Programs
Early AI programs were limited to playing chess or solving algebraic problems. These programs proved slow due to a lack of computational power and data.
1980s: The AI Boom
With the advent of expert systems, AI gathered momentum. These systems worked as a simulated human activity in specific fields, such as medicine and engineering. This time also witnessed the emergence of neural networks, defining the modern scenario of AI.
1990s–2000s: Practical Applications:
AI moved from theory to real-world applications. Some of the eye-catching event milestones included IBM’s Deep Blue defeat of chess champion Garry Kasparov in 1997 and the intelligent search algorithms on which Google and other platforms base their teachings.
The 2010s: The Era of Machine Learning
The explosion of data, combined with advancements in computing power and algorithms, brought AI to new heights. It led to machine learning and deep learning becoming the centerpiece of AI research, offering gains in image recognition, natural language understanding, and autonomous systems.
2020s: The Rise of Generative AI
Generative AI such as GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) and DALL·E has made a unique discovery of new methods of creativity and problem-solving. AI has now become part of every industry, ranging from healthcare solutions to entertainment ones, with footprints across innovation that promise to change the future.
2. Core Concepts of Artificial Intelligence:
Let’s explore the core concepts of AI:
What is AI?


Picture Courtesy: hostadvice.com
Artificial Intelligence is a field of computer science that deals with the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines. This includes the ability to learn, recognize speech, string sentences into an understandable natural language, solve problems, and sometimes create something new.
AI seeks all techniques tries to imitate as well as enhance human cognitive functions at the illusion of independence in the domain of specific situations. AI-powered systems can learn from data, improve over time, and adapt to changing circumstances, mimicking human-like abilities to a remarkable degree.
Key Components and Technologies:
AI operates through a blend of sophisticated components and cutting-edge technologies. Let’s break down the core elements that power AI systems:
A. Machine Learning (ML):
Machine learning manages to learn most without the system having to program them explicitly. In addition to this, ML models rely on algorithms to discover patterns and make decisions on the basis of provided data.
B. Natural Language Processing (NLP):
Enable machines to recognize, interpret, and generate any language spoken by a human. All these could be applications for chatbots and language translation tools, even voice assistants like Alexa and Siri.
C. Computer Vision:
Empower machines to understand and analyze visual data, meaning to categorize space, images, and videos. It has uses in recognition purposes, such as facial recognition, building autonomous vehicles, and studying images in medicine.
D. Neural Networks:
Computational systems imitate the structure of the human brain. Neural networks mainly fall under the category of deep learning, a part of machine learning able to deal completely with unstructured data like text, images, and audio.
E. Robotics:
AI and mechanical systems harmoniously blend to ensure that robots are intelligent enough to do things on their own such as warehouse automation have robotic surgery.
F. Expert Systems:
Expert systems are AI-based computer programs developed to simulate the decision processes of experts in particular fields on the basis of a knowledge base and inference rules.
Machine Learning vs. Artificial Intelligence


Picture Courtesy: readitquik.com
The terms “Machine Learning” and “Artificial Intelligence” are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings:
AI has become an integral part of our lives, influencing how we work, interact, and solve problems. From simplifying everyday tasks to driving innovation across industries, its applications are diverse and impactful. Here’s a look of examples of AI.
Artificial Intelligence in Everyday Life:


Picture Courtesy: claysys.com
AI-powered solutions are everywhere, often making our lives easier in ways we may not even notice:
A. Voice Assistants: Virtual assistants such as Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant employ natural language processing (NLP) to hear commands, then process them, and finally answer.
B. Recommendation Systems: Netflix, Spotify, and Amazon use AI to analyze your preferences and derive personalized content and products.
C. Navigation and Ridesharing: Real-time traffic updates, route optimization, and dynamic pricing depend on AI with applications like Google Maps and Uber.
D. Smart Home Devices: Smart Thermostats, such as Nest, and security cameras that employ AI for automation and face recognition.
E. Social Media Algorithms: Social media feeds, connection suggestions, and content moderation on Instagram, TikTok, and other platforms rely on AI algorithms.
The Latest Inventions In AI:
AI is an evolving field of technology, witnessing developments that stretch far beyond current capabilities:
A. Generative AI Models: ChatGPT, DALL·E, etc. create images, art, and finally human-sounding text, hence revolutionizing content creation.
B. Autonomous Vehicles: AI basically provides self-driving technology to Tesla and Waymo, adopting computer vision, sensor fusion, and decision-making algorithms.
C. AI in Space Exploration: Mission planning, robotic exploration, and analysis of an enormous amount of data from space telescopes with AI nets are researched by NASA.
D. Healthcare Advancements: AI is being used to develop personalized medicine, predict patient outcomes, and assist in complex surgeries using robotic systems.
E. Agricultural Technology: AI-powered drones and sensors help farmers monitor crop health, optimize irrigation, and predict harvest yields.
Applications of AI:
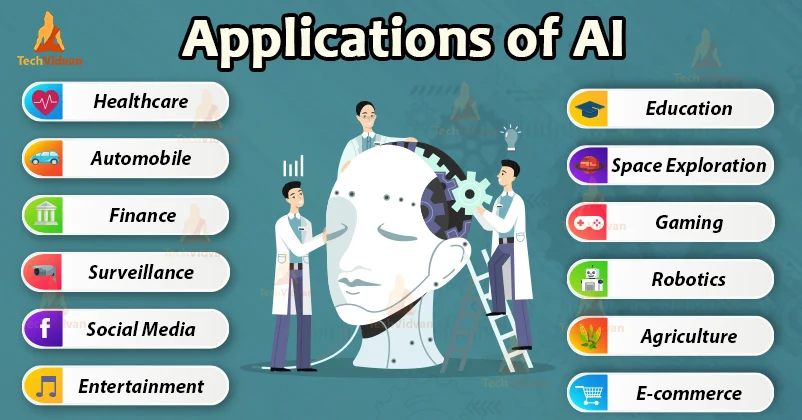

Picture Courtesy: techvidvan.com
Here are some applications of AI:
A. AI in Healthcare: IBM Watson
IBM Watson changed the face of oncology with its analysis of enormous amounts of medical data to offer personalized treatment options for cancer patients and save doctors’ hours while improving outcome results for patients.
B. AI in Retail: Amazon Go
Amazon Go stores use AI-powered cameras and sensors to enable cashier-less shopping. Customers simply pick up items, and their accounts are automatically charged, creating a seamless shopping experience.
C. AI in Finance: JP Morgan Chase
JP Morgan uses AI to analyze financial contracts, reducing hours of manual labor to mere seconds. AI also aids in fraud detection and risk management.
D. AI in Entertainment: DeepMind’s AlphaGo
DeepMind’s AI system, AlphaGo, defeated the world champion in the ancient game of Go. This marked a major milestone in AI, demonstrating its potential to solve highly complex problems.
E. AI in Environment: Google AI’s Flood Prediction
Google AI predicts devastating occurrences with accuracy so that communities might be enabled towards preparation and possible loss of lives.
Artificial Intelligence is revolutionizing industries by providing innovative solutions that enhance efficiency, decision-making, and customer experiences. Let’s explore applications of AI and its impact in key sectors:
A. AI in Healthcare:


Picture Courtesy: yourstory.com
AI in Healthcare is transforming healthcare by enabling faster diagnoses, personalized treatments, and improved patient outcomes:
Medical Imaging and Diagnostics: AI tools such as DeepMind’s healthcare algorithms scrape and find matching codes for virtual disease events like cancer or diabetic retinopathy in patients’ manifests or symptoms.
Personalized Medicine: AI helps analyze genetic makeup, medical history, and lifestyle elements, and crafts personalized treatment plans.
Virtual Health Assistants: Chatbots and virtual assistants like Babylon Health offer patients 24×7 on-call answering and primary-level diagnosis.
Drug Discovery: Drug development by AI, has the ability to comb through, analyze, and interpret massive databases, thus saving time and costs.
Robotic Surgery: The da Vinci Surgical System employs AI to carry out minimally invasive and very precise surgeries, leading to faster recovery periods.
B. AI in Finance:


Picture Courtesy: thefinancialpandora.com
The financial sector has embraced AI to enhance security, improve customer experiences, and streamline operations:
Fraud Detection: AI systems continuously watch transaction patterns to identify and prevent fraud in real time.
Algorithmic Trading: The AI trading algorithm relies on a trading signal that points to an optimal time to trade, thus maximizing profits by analyzing historical and real-time market data.
Personalized Banking: Provides account insights, reminders for bills, and tips on expenses and spending by chatbot, like Erica from Bank of America.
Risk Management: Market risks and financial crises could be predicted using AI by studying data trends and anomalies given to these financial institutions to proactively make decisions.
Credit Scoring: AI enhances the accuracy of credit risk assessments, ensuring fair and efficient lending and borrowing processes.
C. AI in Education:


Picture Courtesy: orangemantra.com
AI is revolutionizing education by making learning more accessible, personalized, and engaging:
Adapted Learning: Platforms such as DreamBox and Coursera have lessons where paces and styles are adapted so that learners have different experiences in education.
Virtual Tutors: AI-driven tools like Squirrel AI can assist students instantly, giving them explanations and more resources for better understanding.
Automated Grading: Grading platforms such as Gradescope using AI help teachers by automatically grading student work, giving them extra time to teach.
Language Learning: Apps like Duolingo deploy artificial intelligence in customizing modules, real-time feedback, and promoting interactive learning.
Education Accessibility: AI tools for speech-to-text and visual aids enable students with disabilities to enjoy the same opportunity to learn as their able-bodied peers.
D. AI in Retail:


Picture Courtesy: goodworklabs.com
AI is enhancing customer experiences and optimizing operations in the retail sector:
Personalized Shopping Experiences: AI analyzes customer data and recommends products according to the preference of the buyer such as Amazon and Sephora.
Inventory Management: AI predicts demand trends, helping retailers manage inventory levels and reduce wastage.
Customer Service Chatbots: AI reviewers give instant feedback, resolve inquiries, and further assist clients in buying goods via developing internal systems.
Visual Search: AI tools like Pinterest Lens allow users to search for products using images instead of text, making shopping more intuitive.
Dynamic Pricing: AI adjusts prices according to demand, competition, and consumer behavior.
5. Artificial Intelligence Jobs and Career Opportunities:
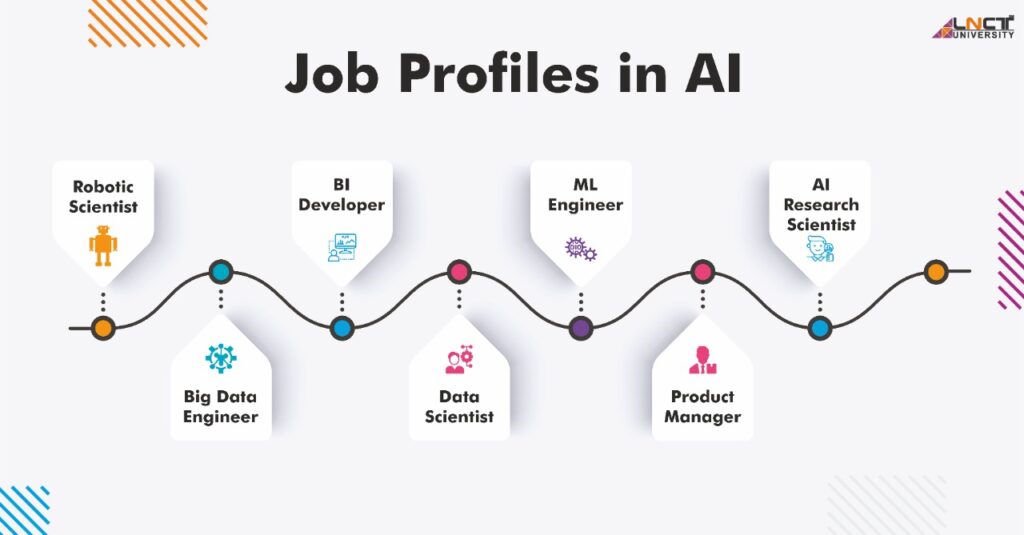

Picture Courtesy: lnctu.ac.in
The rise of Artificial Intelligence has created a booming job market with opportunities across industries. From research and development to practical implementations, AI professionals are in high demand. Let’s delve into the key aspects of pursuing a career in AI.
A. Types of AI Jobs:
AI offers diverse roles catering to different skills and interests:
Machine Learning Engineer: Designs and builds machine learning models, requiring skills in Python, TensorFlow, and statistical analysis.
Data Scientist: Analyzes large datasets to derive insights and develop predictive models, using tools like SQL, R, and Tableau.
AI Research Scientist: Conducts advanced research to create innovative AI solutions, relying on deep learning and programming expertise.
NLP Engineer: Focuses on natural language processing to create chatbots and text analysis tools, leveraging libraries like spaCy and NLTK.
Robotics Engineer: Develops AI-driven robots for various industries, requiring knowledge in embedded systems and mechanical engineering.
AI Ethicist: Ensures responsible AI usage by addressing ethical concerns such as bias and privacy.
Computer Vision Specialist: Works on enabling machines to process and interpret visual data, utilizing image processing and convolutional neural networks.
B. Skills Required for AI Careers:
Success in AI demands a mix of technical expertise, analytical thinking, and domain-specific knowledge:
Programming Proficiency: Strong skills in Python, Java, C++, and R because they help to develop algorithms and software models for artificial intelligence.
Mathematics and Statistics: Familiarity with linear algebra and calculus, as well as some aspects of probability theory, may assist in the construction of an AI model.
Machine Learning Algorithms: Expertise in supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning techniques.
Big Data Handling: Familiarity with tools like Hadoop and Spark for processing large-scale datasets.
Cloud Computing: Experience with platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure for deploying AI solutions.
Communication Skills: Good in explaining AI processes in simple terms to non-technical stakeholders.
Continuous Learning: Look up the latest AI developments, frameworks, and ethical practices.
C. How to Start a Career in AI:
Breaking into the AI field requires strategic planning and consistent effort. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Build a Strong Foundation: Pursue a degree in computer science, data science, or a related field and take specialized AI courses.
Work on Projects: Gain practical experience by creating predictive models, chatbots, or image recognition systems.
Learn AI Tools and Frameworks: Master tools like TensorFlow, Keras, Scikit-learn, and PyTorch.
Join Online Communities: Network with AI professionals through GitHub, Reddit, and LinkedIn groups.
Seek Internships: Apply for AI-focused internships to gain hands-on industry experience.
Build a Portfolio: Showcase your AI projects on platforms like GitHub or personal websites.
Pursue Advanced Education: Consider a master’s degree or certifications like Google AI Certification or IBM AI Engineering Professional Certificate.
Stay Updated: Follow AI news, attend webinars, and engage with the AI community to keep up with trends.
6. Investing in Artificial Intelligence:
Artificial Intelligence is not only transforming industries but also offering lucrative opportunities for investors. Here’s a closer look at how to navigate AI investments effectively.
AI Stocks: The Overview


Picture Courtesy: fool.com
AI stocks refer to shares of companies that either directly develop or utilize artificial intelligence technologies. These companies could be manufacturers of AI hardware, like advanced processors and chips, or they could be software companies that build AI algorithms and platforms. Companies like Nvidia, Alphabet (Google), and Microsoft as leaders in this space, develop generic capabilities that hundreds of thousands of others can use. Firmly established players include companies such as C3.ai that focus all their efforts on AI applications.
In addition, an investor could explore ETFs dedicated to artificial intelligence. These funds could thereby give exposure to diverse companies in the industry while limiting the risk and aiming for great revenue from various applications of artificial intelligence.
An investment in AI stocks is a long-term bet as, given the fact that businesses will quickly adopt AI and automated solutions, the demand for AI technologies will also rise rapidly.
Understanding Artificial Intelligence Stock:
Artificial intelligence stocks can be categorized into two primary groups: pure-play AI companies and diversified tech giants that integrate AI into their operations.
Pure-play companies are those whose business model is entirely based on artificial intelligence technology. C3.ai, which is entirely concerned with AI software for the enterprise sectors across many industries, is one such company.
Diversified tech giants like Amazon, Apple, or IBM would not be focused as AI companies. They have considerable interest in artificial intelligence research and development.
The key considerations for an investor looking at AI stocks include the growth in revenue from AI for specific companies, investment in research and development, and competitive positioning in the AI market. The success of AI companies is often tied to their ability to innovate, keep up with technological advancements, and capitalize on the growing demand for AI applications.
AI Penny Stocks: Risks and Rewards


AI penny stocks are shares of smaller companies in the AI sector, typically trading for less than $5 per share. These stocks can be an attractive option for investors seeking high-risk, high-reward opportunities, as smaller companies in emerging sectors often have the potential for rapid growth. However, investing in AI penny stocks comes with significant risks.
Rewards: The appeal of AI penny stocks lies in their potential for explosive growth. Early-stage companies that develop innovative AI technologies can see their stock prices rise sharply as their products gain traction in the market. For investors who manage to enter these stocks early, the financial rewards can be substantial.
Risks: Penny stocks are often highly volatile, with price fluctuations that can be difficult to predict. These companies are typically less stable than their larger counterparts, which can lead to liquidity issues and larger-than-usual swings in stock prices. Additionally, penny stocks are more prone to speculative trading, which can distort the true value of the company. Investors in AI penny stocks must conduct extensive research to evaluate the viability of the company’s AI technologies, market demand, and overall financial health.
Despite the risks, AI penny stocks offer an intriguing opportunity for investors who are willing to take on higher risk in exchange for the chance to invest in promising, early-stage companies. However, careful research and diversification strategies are essential to mitigate the risks associated with penny stocks.

Picture Courtesy: nbkomputer.com
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has transformed the way we interact with technology, enabling machines to mimic human intelligence and perform tasks with remarkable precision. From streamlining processes to enhancing user experiences, AI’s applications are vast and impactful. Its ability to process large volumes of data, learn from patterns, and adapt to new inputs makes it a powerful tool for solving complex problems across various industries. Here are some of the key benefits of AI:
A. Efficiency and Automation:
On the one hand, AI automation saves businesses worldwide time and money. Repeated and mundane tasks can be automated by machine learning algorithms or robotics. AI systems manage workflow, inventory, and supply chains without human touch. Consequently, they become more productive while maintaining the highly strategic roles of human workers.
B. Enhanced Decision Making:
AI analyzes data on a greater scale and faster speed than ever before and produces actionable information for decision-making. Through processing historical and real-time data, these tools can forecast trends, identify risks, and provide recommendations aligned with business needs. This results in informed decisions, reducing the probability of errors.
C. Personalization and Customer Experience:
AI customizes interactions with customers as well as anticipates their demands. Whether through product recommendations appearing on an e-commerce website or 24/7 support provided through AI-enabled chatbots, organizations use technology to present personalized experiences to customers. It finally creates trust, loyalty, and a competitive edge in the market.
8. Artificial Intelligence Resources:
Whether you’re a beginner eager to dive into AI or a professional looking to enhance your expertise, a wealth of resources is available to help you. From books to online courses, staying updated on AI developments is essential for mastering this transformative field. Here’s a breakdown of some key AI resources:
A. Books: Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach


Picture Courtesy: in.pinterest.com
Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach is written by Stuart Russell and Peter Norvig, gives a definitive guideline to the principles and application of AI. This massive text covers every theoretical material of AI from search algorithms to what it relates with, machine learning, robotics to what it can do, and natural language processing. However, again it remains a genuine material for beginners and professionals alike in understanding both theoretical and practical aspects of AI.
B. AI News and Updates:
It is really important to keep up with the latest trends and innovations in AI. Sites like AI News, MIT Technology Review, and OpenAI Blog are good resources for keeping up with AI advancements, breakthroughs in research, and industry applications. Signing up for newsletters or following these AI influencers on sites like LinkedIn and Twitter can also keep you updated.
C. Online Courses and Certifications:
Several online platforms offer AI courses for all skill levels:
Coursera: Offers courses like “Machine Learning” by Andrew Ng, a great starting point for beginners.
edX: Features programs such as “AI for Everyone” and advanced courses like “Artificial Intelligence MicroMasters.”
Udemy: Provides a wide range of AI courses, from beginner-friendly to advanced deep learning tutorials.
Google AI and TensorFlow: Free resources and courses for understanding machine learning and building AI applications.
Completing these certifications can boost your understanding of AI concepts and enhance your career prospects in the field.
9. Conclusion and Future of Artificial Intelligence:

Picture Courtesy: aiecommerce.com
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer just a futuristic concept—it’s a transformative force shaping industries, economies, and daily life. From improving efficiency and decision-making to revolutionizing customer experiences, AI has proven its value across diverse domains. As AI continues to evolve, it will unlock new possibilities, addressing challenges in healthcare, education, transportation, and beyond. However, with its potential comes the need for ethical considerations, transparency, and robust frameworks to guide its development and implementation.
Future of AI: What Lies Ahead?
Let’s see what lies ahead in the future of AI:
A. Enhanced Human-AI Collaboration:
The future will see AI acting as a complementary partner to humans, amplifying our capabilities rather than replacing us. From AI-powered tools that assist in creative processes to robotic systems that support physically demanding tasks, collaboration will redefine work and productivity.
B. AI in Healthcare:
AI is set to revolutionize healthcare through personalized medicine, predictive analytics, and advanced diagnostics. Technologies like AI-driven drug discovery and robotic surgery will become more widespread, improving patient outcomes and accessibility.
C. Autonomous Systems and Smart Cities:
The rise of autonomous vehicles, drones, and smart infrastructure will redefine urban living. AI will play a pivotal role in reducing traffic congestion, optimizing energy consumption, and ensuring public safety in smart cities worldwide.
D. AI and Education:
Education will be transformed by AI through adaptive learning platforms, personalized curriculums, and virtual tutors. These innovations will make learning more accessible, efficient, and tailored to individual needs, bridging educational gaps globally.
E. Ethical AI and Regulation:
As AI becomes more integrated into society, there will be a stronger focus on developing ethical AI systems. Governments and organizations will work to establish guidelines ensuring fairness, accountability, and transparency in AI applications.
F. Quantum AI:
The integration of AI with quantum computing holds immense potential for solving problems currently beyond the scope of traditional computing. From complex simulations to advancements in cryptography, Quantum AI could lead to groundbreaking discoveries.
G. AI-Driven Sustainability:
AI will be instrumental in tackling global challenges like climate change, resource management, and biodiversity conservation. By analyzing environmental data, AI can help create sustainable solutions, monitor ecosystems, and predict natural disasters.
A World of Possibilities:
The future of AI is as exciting as it is unpredictable. While we continue to innovate and leverage AI’s potential, it’s equally important to address challenges such as data privacy, algorithmic bias, and job displacement. By fostering collaboration between researchers, policymakers, and industry leaders, we can ensure AI is developed responsibly and inclusively. The next frontier of AI will be defined by how effectively we balance its immense potential with its inherent responsibilities, creating a future where technology truly benefits humanity.
AI holds the promise of reshaping our world, making it smarter, more efficient, and interconnected. However, as we embrace its potential, we must also navigate challenges like ethical use, data privacy, and societal impact. The future of AI depends on how responsibly we innovate and integrate it into our lives.
What’s your take on AI? Do you see it as a tool for progress, or do you have concerns about its rapid growth? Share your thoughts in the comments below!
For more insights and updates on Metaverse, DeFi, Blockchain, NFT & Web3, be sure to subscribe to our newsletter. Stay informed on the latest trends and developments in the decentralized world!










