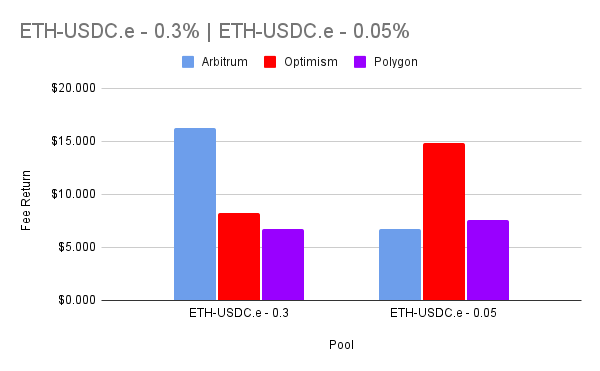
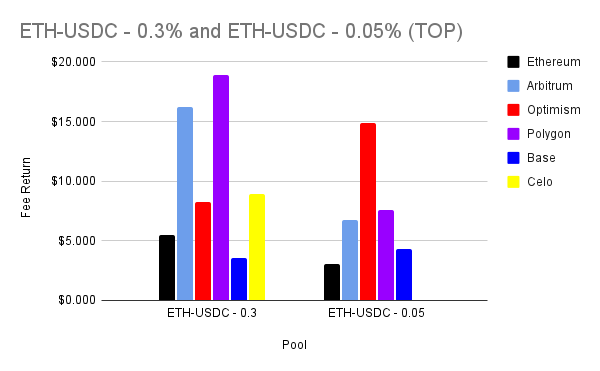
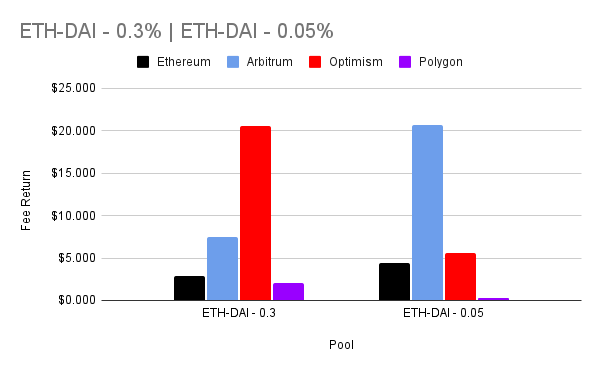
What is Account Abstraction?
Account abstraction is an innovative concept in blockchain that seeks to unify and enhance the functionality of user accounts within a decentralized system. In the Ethereum network, two types of accounts currently exist:
Externally Owned Accounts (EOAs): Controlled by private keys and usually belonging to individuals or entities.
Contract Accounts: Smart contracts that are executed based on specific logic written in their code.
Account abstraction seeks to unify the two types of Ethereum accounts—EOAs (Externally Owned Accounts) and smart contract accounts—into a single, more user-friendly model. This is done by allowing smart contracts to initiate and validate transactions.
In simple terms, this means that instead of relying solely on private keys (like with EOAs), smart contracts can now manage and execute transactions on behalf of users, offering greater flexibility and enabling new features such as customizable security models, automated and gasless transactions, meta-transactions, and enhanced privacy. These innovations simplify user interactions and expand the possibilities within the Ethereum ecosystem.
What are the problems we are facing? Why do we need it?
The Ethereum network’s current structure faces some limitations:
User Experience: EOAs require private keys and gas fees in Ether, creating friction for new users who may find wallet security and gas concepts complex.
Security Risks: The binary nature of private keys makes them susceptible to loss or theft, leading to irrevocable loss of funds.
Limited Features: EOAs lack programmability, preventing the implementation of advanced features like multi-signature wallets or daily transaction limits.
Account abstraction aims to address these issues, improving the network’s usability, security, and functionality.
Approaches to Implement Account Abstraction: Pros and Cons
1. Protocol-Level Changes
Involves changing the Ethereum protocol to enable native smart contract wallets. This approach demands consensus across the entire Ethereum network.
Pros: Fully integrated and standardized solution, potentially highly efficient.
Cons: Slow adoption, requires hard forks, and poses compatibility issues.
2. Layer 2 Solutions
Layer 2 networks can implement custom transaction validation logic while offloading transaction processing.
Pros: Fast and flexible, allowing experimentation without altering the main Ethereum protocol.
Cons: Requires complex bridging and may not fully resolve core issues with EOAs.
3. ERC-4337 (Ethereum Request for Comments)
Proposes an account abstraction implementation entirely at the application level without requiring protocol changes.
Pros: Backward-compatible, flexible, and leverages existing infrastructure.
Cons: Requires an additional bundler infrastructure and new transaction flow.
What Is ERC-4337 and Why Is It the Best Implementation?
ERC-4337 introduces a new model for handling transactions, known as UserOperation objects. Instead of sending transactions directly to the Ethereum blockchain, users sign UserOperation objects that bundlers aggregate and submit to the blockchain. This system allows smart contract wallets to securely initiate transactions without depending on the existing transaction flow.
Benefits:
Programmability: Allows developers to implement custom validation logic, enabling features like social recovery and multi-signature wallets.
Reduced Costs: Bundling transactions can lead to optimized gas usage.
Backward Compatibility: Can operate alongside EOAs, offering a seamless transition.
Specs, Details and Architecture of ERC-4337
Components:
1. User:
Off-chain: Creates and signs a UserOperation, which contains the transaction data.
2. UserOperations:
Off-chain: Represents the transaction data, similar to the structure of a regular transaction.
3. Bundler:
Off-chain: Collects multiple UserOperations.
On-chain: Packages them into a batch transaction and submits it to the EntryPoint contract.
4. EntryPoint Contract:
On-chain: Manages the execution of UserOperations and ensures consistency across the transactions.
5. Paymaster:
On-chain: Can sponsor transaction fees by paying for gas on behalf of users.
Workflow:
A user creates a UserOperation off-chain and then signs it.
The bundler collects UserOperations from different users and submits them to the EntryPoint contract.
The EntryPoint contract verifies and executes each UserOperation, deducting gas fees appropriately.
What Are Bundlers in Detail?
Bundlers are specialized actors in the ERC-4337 architecture. Their responsibilities include:
Aggregation: Collects multiple UserOperations and aggregates them into a single batch transaction.
Submission: Sends the aggregated transaction to the EntryPoint contract for execution.
Fee Collection: Takes care of gas fees by deducting them from UserOperations or through external sponsorship mechanisms.
Eth Infinitism Bundler
Eth Infinitism is a reference implementation of a bundler designed to work with the ERC-4337 account abstraction standard. It provides developers with a tool to bundle transactions in a production-ready environment.
Github: https://github.com/eth-infinitism/account-abstraction
Steps on How to Run Eth Infinitism Bundler with Geth
Steps:
1. Start Geth docker container using this command:docker run –rm -ti –name geth -p 8545:8545 ethereum/client-go:v1.10.26 \
–miner.gaslimit 12000000 \
–http –http.api personal,eth,net,web3,debug \
–http.vhosts ‘*,localhost,host.docker.internal’ –http.addr “0.0.0.0” \
–ignore-legacy-receipts –allow-insecure-unlock –rpc.allow-unprotected-txs \
–dev \
–verbosity 2 \
–nodiscover –maxpeers 0 –mine –miner.threads 1 \
–networkid 1337
2. Clone Eth-Infinitism Guthib repo – https://github.com/eth-infinitism/bundler
3. Change directory and run
cd bundler
yarn && yarn preprocess
4. Now we will deploy contracts that came with bundler using hardhat –
yarn hardhat-deploy –network localhost
5. We will start the bundler –
yarn run bundler (or yarn run bundler –unsafe, if working with “hardhat node”)
Now your bundler is active on local url http://localhost:3000/rpc
6. To run a simple test, do –
yarn run runop –deployFactory –networkhttp://localhost:8545/ –entryPoint 0x0000000071727De22E5E9d8BAf0edAc6f37da032
The runop script:
deploys a wallet deployer (if not already there)
creates a random signer (owner for wallet)
determines the wallet address, and funds it
sends a transaction (which also creates the wallet)
sends another transaction, on this existing wallet
(uses account[0] or mnemonic file for funding, and creating deployer if needed)
Conclusion
In this article, we delved into the concept of account abstraction in Ethereum, an innovative approach designed to enhance blockchain functionality by merging externally owned accounts (EOAs) with contract accounts. We examined the limitations of the current Ethereum account model, explored various implementation strategies including the prominent ERC-4337 standard, and discussed the significant roles of bundlers like the Eth Infinitism Bundler in optimizing transaction processes.
This exploration provided a comprehensive understanding of how account abstraction can facilitate more secure, user-friendly, and programmable interactions within the Ethereum ecosystem, alongside practical insights on implementing these concepts using Eth-Infinitism bundler with Geth.