A Bitcoin layer 2 is any offchain network, system, or technology built on top of the Bitcoin blockchain to help extend its capabilities.
Since its inception in 2008, Bitcoin has become the focal point of the verifiable web as the first decentralized cryptocurrency, remaining the largest one by market capitalization. However, Bitcoin’s growth has faced challenges due to the network’s limited scalability, often resulting in high transaction fees and network congestion.
The recent introduction of ordinals, BRC-20 tokens, and other Bitcoin-native onchain applications has further exacerbated these issues, where—especially during peak times—Bitcoin can become impractical for everyday use. These ongoing scalability challenges highlight the immediate need for Bitcoin scaling solutions such as layer-2 networks.
In this post, we discuss what Bitcoin layer 2s are, how they work, and how they can benefit from industry-standard oracle services.
How Do Bitcoin Layer 2s Work?
The Bitcoin network takes about 10 minutes to finalize a single block of transactions—only seven transactions per second (TPS) on average. Scaling the Bitcoin blockchain directly isn’t an option, as it would require compromising either security or decentralization per the blockchain scalability trilemma.
It’s worth noting that the limited core functionality (i.e., a global, censorship-resistant decentralized currency) helps make the Bitcoin network so tamper-proof and robust, and a significant technological breakthrough of the 21st century. However, this narrow focus limits the network’s usability in everyday scenarios and limits developers’ ability to launch new applications on Bitcoin. Enter layer 2s.
A Bitcoin layer 2 is any offchain network, system, or technology built on top of the Bitcoin blockchain that helps extend its capabilities. Layer-2 networks can introduce improvements such as greater transaction throughput, reduced fees, and programmability through smart contracts. A key requirement for a network to be considered a layer 2 is that it must inherit the security of the blockchain it is built on—in this case, Bitcoin. In the case of Bitcoin layer 2s, this means that transaction data is verified and confirmed by the Bitcoin blockchain rather than a separate set of nodes.
Layer-2 networks can vary considerably in how they achieve this increased scalability, but a common denominator between layer-2 environments is that when looking to settle on the base chain, they must provide some kind of cryptographic proof to the blockchain on the integrity of the proposed state change, either preemptively or retroactively.
If you’d like a deep dive into how layer 2s work, read What Is Layer 2?.
Types of Bitcoin Layer 2s
There are several types of Bitcoin scalability solutions that can be categorized as layer 2s, though some exist in a gray area regarding their classification as true layer-2 solutions. Note that Bitcoin scalability is an ongoing area of research, and new solutions and technologies may emerge in the future to address some of the limitations of current Bitcoin layer-2 technologies.
State Channels
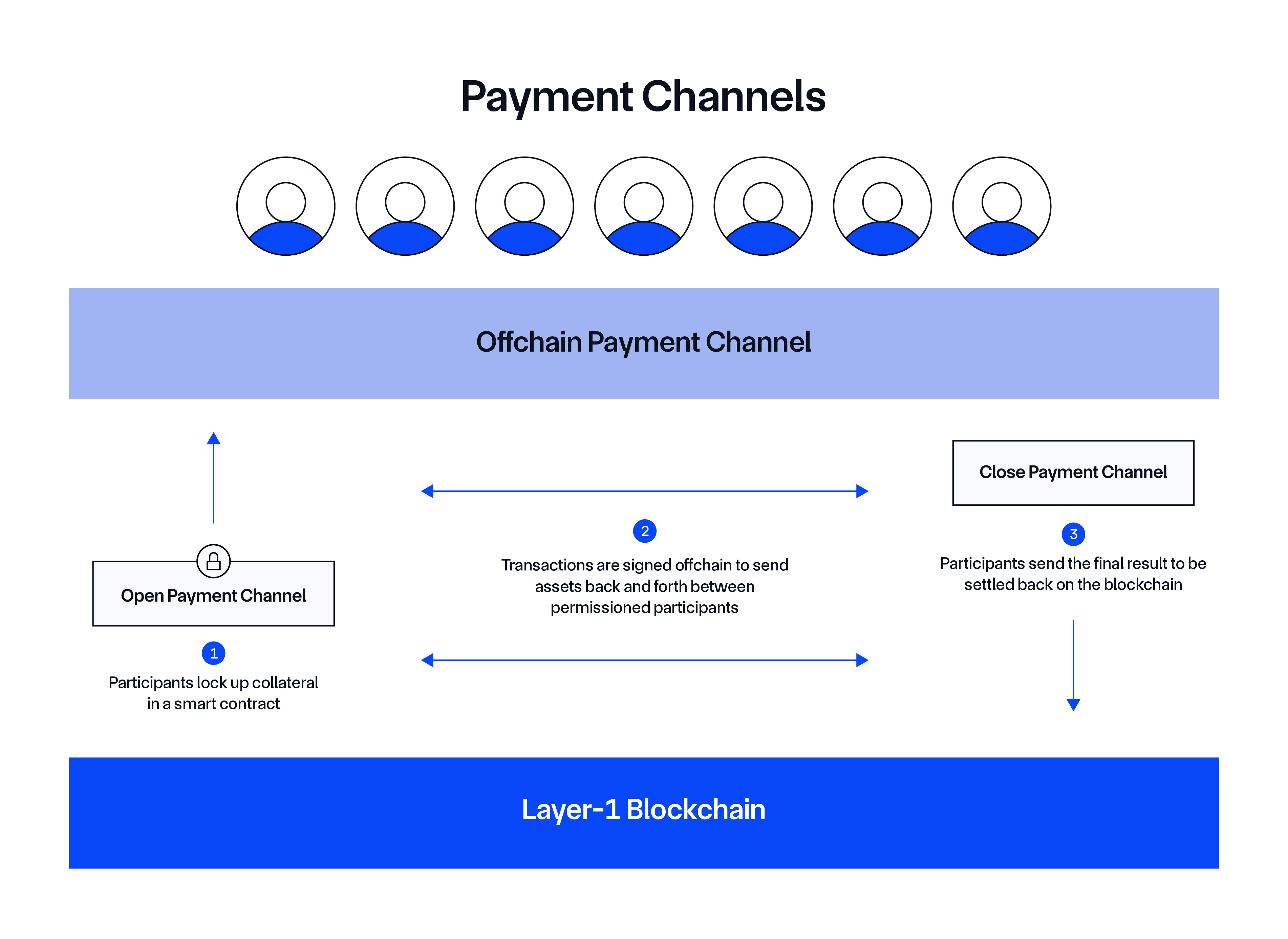
State channels enable users to bypass high transaction fees by moving transactions offchain, where two parties lock a certain amount of bitcoin into a multisig to send and receive payments. These channels then maintain records of all transactions that occur within them until they are closed. When the parties are done transacting, they sign and broadcast the final state of the channel to the Bitcoin blockchain.
State channels keep all transactions within them offchain, only reporting the opening and closing balance of participants to the Bitcoin network. This allows participants to make transactions without having to pay Bitcoin mainnet fees for each transaction.
State channels are similar to payment channels in the Bitcoin Lightning Network, but they also support more complex transactions other than micropayments.
Sidechains
A sidechain is an independent blockchain with its own consensus mechanism that connects to Bitcoin via a two-way peg, allowing the transfer of assets or balances between the two chains. While sidechains often use bitcoin as their native currency, they can also issue their own native tokens.
Operating as separate blockchains, sidechains offer faster transactions and additional features like smart contracts. Because sidechains have their own validator set, they are not always considered true layer-2 solutions, as transactions aren’t necessarily ultimately verified by the Bitcoin network. However, some sidechains may tap into Bitcoin’s security or periodically settle on the main chain.
Rollups
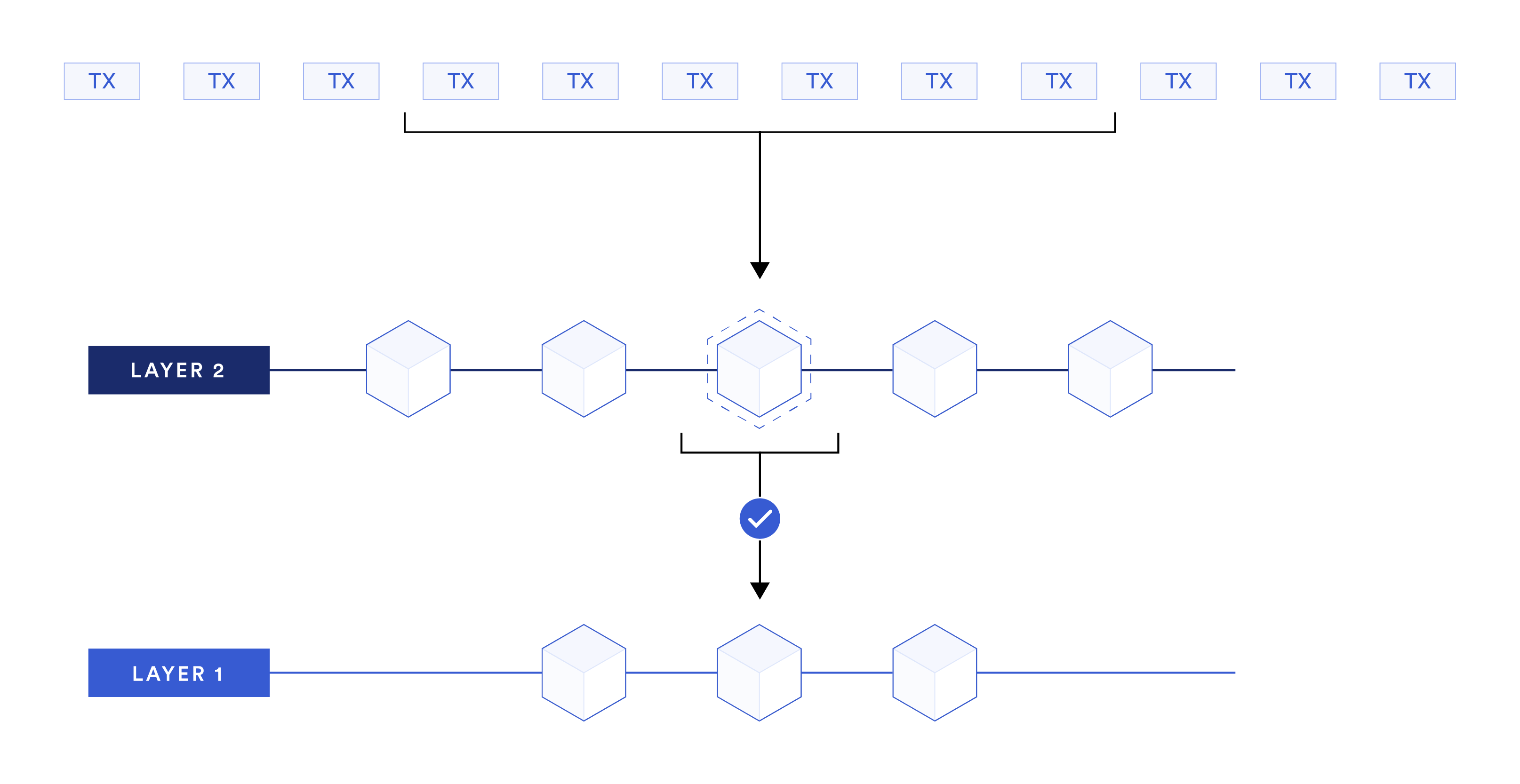
Bitcoin layer-2 rollups move transaction execution and data off the main Bitcoin blockchain to a separate rollup chain or layer while still anchoring to Bitcoin for data availability and consensus.
Rollup technology involves executing transactions on the rollup chain, compressing data, and anchoring to the Bitcoin mainnet. Users submit transactions to be executed on the rollup chain rather than directly on the Bitcoin blockchain. The rollup chain then processes these transactions and updates account balances accordingly.
After processing a batch of transactions offchain, the rollup compresses the transaction data into a compact cryptographic proof or commitment, representing the net effect of all those transactions. This compressed proof is periodically submitted to the Bitcoin blockchain as a single transaction, and some kind of verification mechanism on Bitcoin then validates and applies the changes represented by the rollup proof.
Benefits of Bitcoin Layer 2s
Bitcoin layer 2s offer several benefits:
Greater scalability—Bitcoin layer 2s effectively increase the transaction throughput and speed of Bitcoin by processing transactions offchain and then settling them on the main chain, depending on the solution.
Reduced fees—Bitcoin layer 2s enable lower transaction costs, unlocking use cases secured by Bitcoin that wouldn’t be feasible on the main Bitcoin network, such as micropayments.
Programmable smart contracts—Although Bitcoin was not initially designed to support smart contracts, layer-2 solutions can introduce this functionality, enabling the creation of complex decentralized applications and novel programmable financial instruments built on Bitcoin.
Deeper liquidity—Bitcoin layer 2s can improve liquidity and access to Bitcoin, unlocking DeFi on Bitcoin with enhanced liquidity, capital efficiency, and increased access.
Bitcoin Layer 2 vs. Ethereum Layer 2
The utility of layer-2 solutions lies in how they tap into the security of the main chain while increasing its scalability. In this way, Bitcoin and Ethereum layer 2s are quite similar—both seek to introduce enhanced scalability without making changes to the base layer. However, Bitcoin and Ethereum layer 2s differ significantly in their technical implementation, as Bitcoin and Ethereum themselves are designed for distinct purposes.
Accelerating Bitcoin Layer 2 Adoption
State channels, sidechains, rollups, and other layer-2 solutions are all methods of approaching the blockchain scalability problem in different ways—supporting both the growing adoption of onchain applications and enhanced use cases and user experiences.
The Chainlink platform has underpinned the DeFi ecosystem since its inception, fulfilling the need for high-quality data, compute, and interoperability services that help developers create fully-fledged decentralized applications. In many cases, integrating Chainlink has helped layer-1 and layer-2 ecosystems bootstrap their growth with battle-tested Chainlink infrastructure, attracting both new developers and users. With the emerging ecosystem of Bitcoin layer-2 scalability solutions, the need for high-quality data and other oracle services will also grow in the Bitcoin ecosystem.
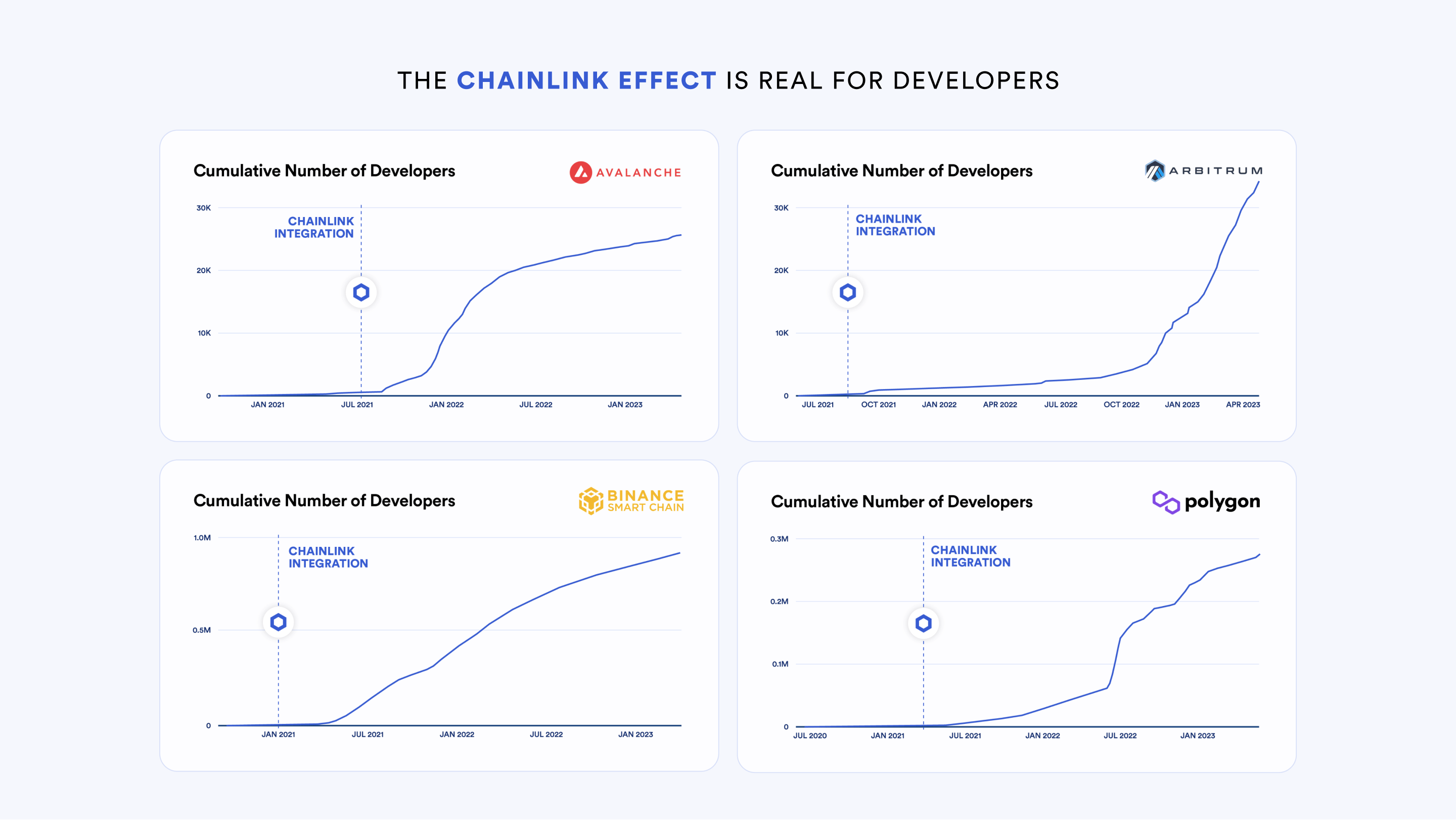
A significant advantage of adopting the Chainlink platform is that once an app uses a single Chainlink service, there are little-to-no additional trust assumptions for using other Chainlink services since they are all built upon the same time-tested oracle infrastructure. And every new service built on top of Chainlink adds more value for all existing users. This is why blockchains are increasingly joining the Chainlink Scale program as a way to accelerate the growth of their application ecosystem. An integration with Chainlink can bring multiple services to a single blockchain and subsequently drive a surge in developer activity.
To learn more about Chainlink, visit chain.link, subscribe to the Chainlink newsletter, and follow Chainlink on Twitter, YouTube, and Reddit.